The UAE Council for Digital Wellbeing and the UAE National Programme for Artificial Intelligence this week published a Deepfake Guide to help raise social awareness about the technology. But what are deepfakes and are they all bad? Here are my top 9 deepfake video predictions!
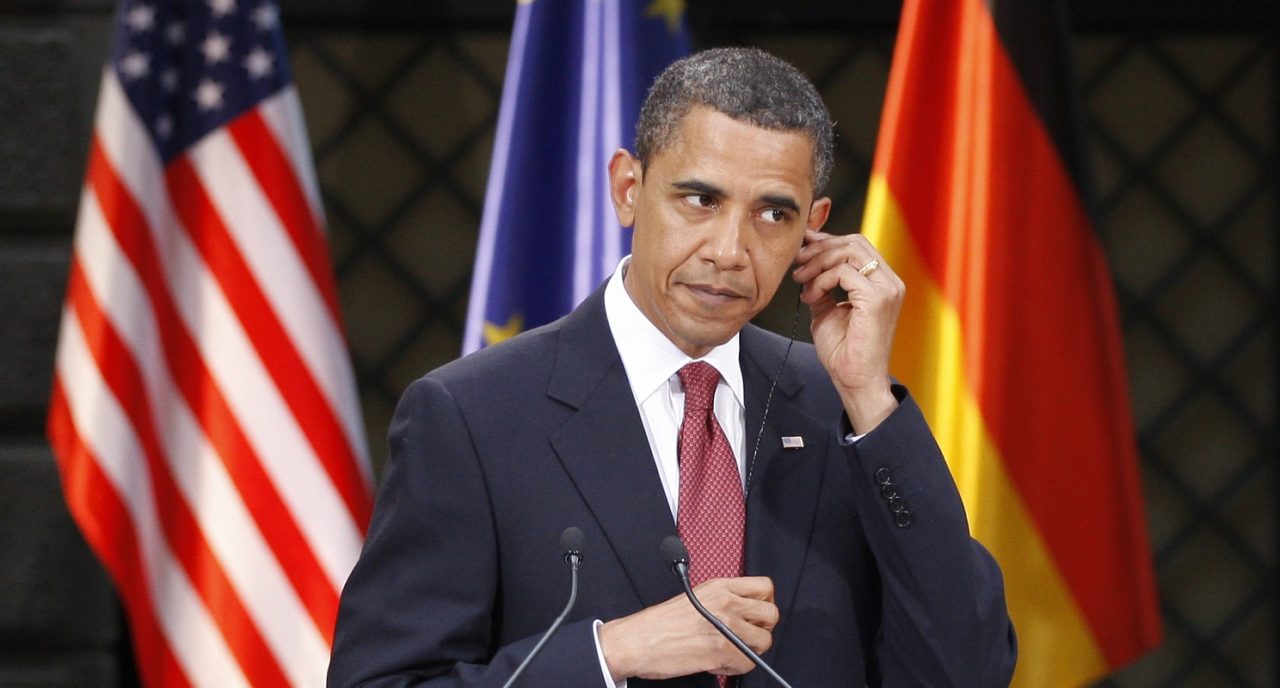
Deepfake videos first hit the headlines six years ago when Stanford University created a model that could change the facial expressions of famous people in video. In 2017, University of Washington researchers released a fake video of former President Barack Obama making a speech using an artificial intelligence neural network model. It wasn’t long before consumers could create their own deepfake videos using a variety of tools, including deepfakesweb.com’s free online deepfake video application. Deepfake videos have now become commonplace circulating on social media of presidents, actors, pop stars and many other famous people.
So, what’s all the fuss about? Simply, that fakes of any nature can be used to deceive people or organisations with malicious intent or for ill-gotten gains. This could include cyber-bullying, fraud, defamation, revenge-porn or simply misuse of video for profit. It perhaps comes as no surprise that a 2019 study found that 96 per cent of all deepfake videos online were pornographic.
However, using technology to produce fakes is not a new thing. The swift rise of the photocopier in the 1970s and 80s allowed office workers all over the world to alter and reproduce copies of documents, letters and certificates. The ease with which printed information could be copied and altered, prompted changes in laws, bank notes, business processes and the use of anti-counterfeit measures such as holograms and watermarks.
Like photocopying, deepfake video technology is getting better and better at what it does as time goes on, but at a much faster speed of development. This means that the cutting edge of deepfake technology is likely to remain ahead of AI systems developed to detect fake video for a long time to come.
Any technology can be used for good or evil. However, in a few short years deepfake technology has got itself a terrible reputation. So, what is it good for? My take is that deepfake video technology – or synthetic video for the commercially-minded – is just one aspect of artificial intelligence that is going to change the way that we use video, but it will be an important one. Here are my top nine deepfake video predictions.
1. Deepfake tech is going to get easier and easier to use
It’s now quite easy to create a deepfake video using the free and paid-for consumer apps that are already in the public domain. However, as the world learns to deal with deepfake video, the technology will eventually be embedded into more and more applications, such as your mobile device’s camera app.
2. Deepfake technology’s reputation is going to get worse
There’s an awful lot of potential left for deepfake scandal! The mere fact that developers are creating software that can detect deepfake video, means that the small percentage of deepfake video that can not be identified as fake may be seen as having a virtual rubber stamp of approval! And believing that a influential deepfake video is authentic is where the problem starts.
3. Policymakers are going to struggle to regulate usage
Artificial intelligence is testing policymakers’ ability to develop and implement regulation like no other force before it. The issues are the most obvious when deepfakes are used for criminal activitiy (the courts are already having to deal with deepfake video). In the near future, regulators are also going to have to legislate on the rise of ‘legitimate’ use, seamlessly altering video for education, business, government, politics and other spheres.
4. One:one messaging
One of the most exciting possibilities is how deepfake modelling might be used to create personalised one:one messaging. Today, it’s possible for you to create a video of you voicing a cute animation via an iPhone. Creating and sending a deepfake video of your real self will soon be as easy as sending a Whatsapp message. If that sounds too frivolous, imagine that you’re stuck in a meeting and want to send a message to your five year-old.
5. Personalisation at scale
As the technology becomes easier to use and manipulate, and as the processing power becomes available to automate that process further, we’re going to be able to create extremely lifelike deepfake videos – or synthetic videos, if you rather – at scale. London-based Synthesia is already testing personalised AI video messages. That will open the doors for marketers to personalise a new generation of video messages at scale and deliver a whole new experience to consumers. Imagine if every new Tesla owner received a personal video message from Elon Musk (well, ok, imagine something else then!).
6. Deepfakes on the campaign trail
As marketers get their hands on new tools to create personalised video messages for millions, then there may be no stopping political parties from doing so too. Has your candidate been banned from social media? No problem! Send out a personalise appeal for support directly to your millions of supporters! In fact, this is one use that I could see being banned outright before it even gets started.
7. Video chatbots
There are already a number of developers creating lifelike synthetic video avatars for use as customer service chatbots, including Soul Machines and Synthesia. As AI generated avatars become more lifelike, the lines between different types of video avatars and AI altered deepfake videos are going to blur. The decisions on what platform, what AI technology, what video experience and what type of voice to add, are going to be based on creative preferences or brand goals, not technology.
8. Deepfake entertainment
Although some deepfake videos can be entertaining, their novelty value already seems to be fading. In the future, whether a deepfake is entertaining or not will depend on the idea and creativity behind it. We seem to be headed for an some kind of extended reality music world, where music, musicians, voices, characters and context are all interchangeable, manipulated by increasingly sophisticated technology. The Korean music industry is already investing heavily in virtual pop stars and mixed reality concerts. Deepfake representations will not be far behind. After all, they’re already reading the news! The Chinese national news service (Xinhua) has been using an AI news anchor for the past two years.
9. Your personal AI avatar
In 2019, Biz Stone co-founder of Twitter and Lars Buttler, CEO of San Francisco-based The AI Foundation, announced that they were working on a new technology that would allow anyone to create an AI avatar of themselves. The AI avatar would look like them, talk like them and act like them, autonomously. In comparison, creating personal avatars using deepfake technology (i.e. manipulating already existing video) could be a lot easier to do. It remains to be seen how long it will take before we have the capability to have our own autonomous AI avatars, but creating our own personal AI video chatbot using deepfake tech is just around the corner!
I hope that you liked my top deepfake video predictions! But, what do you think? Will AI altered deepfakes and AI generated video avatars soon compete for our attention? Or will one negate the need for the other? And how long do you think it will be before consumers are over-targeted by personalised AI generated video? Be the first to comment below and win a tube of Pringles!
This article was first posted on Linkedin. If you’re interested in this sort of thing, I also wrote about deepfakes for The National a couple of years ago. You can find that article here.